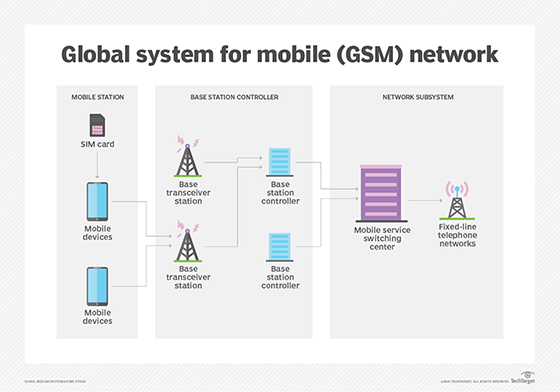
What is GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)?
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a digital mobile communication standard applied widely in Europe and other parts of the world. Globally compatible, GSM is more popular than another 2G mobile standard: code-division multiple access (CDMA), which is only available in a few countries. While CDMA is tied to a specific mobile phone and […]
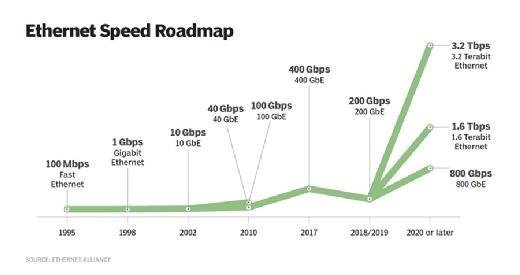
Read MoreWhat is 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet)?
1000BASE-T is a Gigabit Ethernet standard that operates at a speed of 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) over copper wiring. One Gb is equivalent to 1,000 megabits per second (Mbps). The standard uses four pairs of Category 5 (Cat5) or higher unshielded twisted pair (UTP) copper cables to achieve the gigabit data rate. The “T” […]
Read MoreWhat is shielded twisted pair (STP) and how does it work?
Shielded twisted pair (STP) is a kind of cable made up of smaller wires where each small pair of wires is twisted together and has an outer coating to electrically shield it. STP is used for telephone and local area network (LAN) wiring. Shielded means it has an outer covering or shield that functions as […]
Read MoreWhat is ping and how does it work?
Ping (Packet InterNet Groper) is a basic internet program that enables a user to test and verify if a particular destination Internet Protocol (IP) address is reachable and can respond to network requests. Ping is based on Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) and is one of the most widely used tools for diagnosing internet and […]
Read MoreWhat is MIMO (multiple input, multiple output)?
MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) is an antenna technology for wireless communications in which multiple antennas are used at both the source (transmitter) and the destination (receiver). The antennas at each end of the communications circuit are combined to minimize errors, optimize data speed and improve the capacity of radio transmissions by enabling data to […]
Read MoreHow to ensure OT secure remote access and prevent attacks
Operational technology underpins the infrastructures that support critical industrial systems worldwide. Protecting these infrastructures has become more challenging as internet connectivity has been introduced to these environments and as cyberthreats become more potent. Many OT security threats target remote access. Although remote access is a necessity for most industrial systems, this interconnectivity ushers in […]
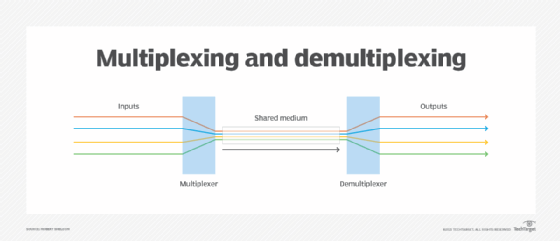
Read MoreWhat is multiplexing and how does it work?
Multiplexing, or muxing, is a way of sending multiple signals or streams of information over a communications link at the same time in the form of a single, complex signal. The goal is to enhance the channel’s transmission efficiency and speed, even over long distances. When the composite signal reaches its destination, a process called […]
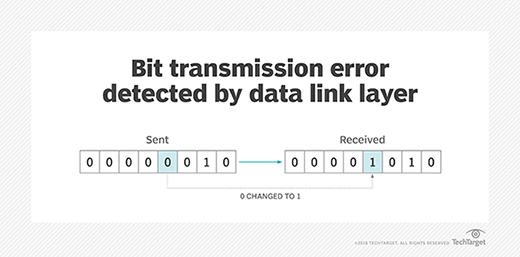
Read MoreWhat is the data link layer in the OSI model?
The data link layer is the protocol layer in a program that handles how data moves in and out of a physical link in a network. It is Layer 2 in the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) architecture model, and its main purposes are to facilitate data transfers between network entities and to ensure reliable error-free […]
Read MoreWhat is port address translation (PAT)?
Port address translation (PAT) is a type of network address translation (NAT) that maps a network’s private internal IPv4 addresses to a single public Internet Protocol address by using network ports. NAT is a process that routers use to translate internal, nonregistered IP addresses to external, registered IP addresses. PAT differs from other forms of […]
Read MoreWhat is a northbound interface/southbound interface?
A northbound interface (NBI) is an application programming interface (API) or protocol that allows a lower-level network component to communicate with a higher-level or more central component; conversely, a southbound interface (SBI) allows a higher-level component to send commands to lower-level network components. Northbound and southbound interfaces are most associated with software-defined networking (SDN), but […]
Read More