What is IoT security?
IoT security is the technology segment focused on safeguarding connected devices and networks in the internet of things. IoT involves adding internet connectivity to a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals and people. Each thing has a unique identifier and the ability to automatically transfer data over a network. However, […]
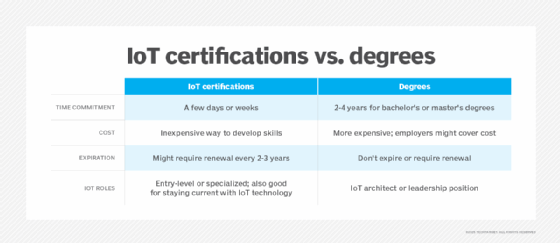
Read More11 top IoT online courses in 2025 (free and paid)
IoT is one of the most transformative technologies of the 21st century. It’s powering advancements across industries, such as healthcare, transportation and manufacturing, as well as the supply chain. As a key driver of Industry 4.0, IoT enables smart automation and data-driven decision-making. According to Fortune Business Insights, the market is projected to grow […]
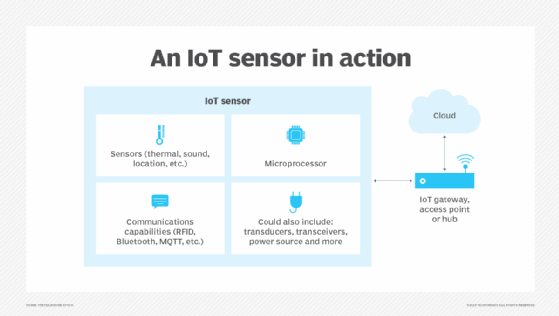
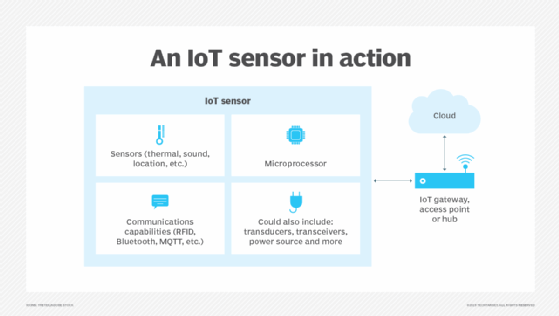
Read MoreWhat is sensor data? Examples of sensors and their uses
Sensor data is the output of a device that detects, analyzes and responds to some type of input from the physical environment. The output is used to provide information to an end user or as input to another system or to guide a process. Sensors can be used to detect just about any physical element. […]
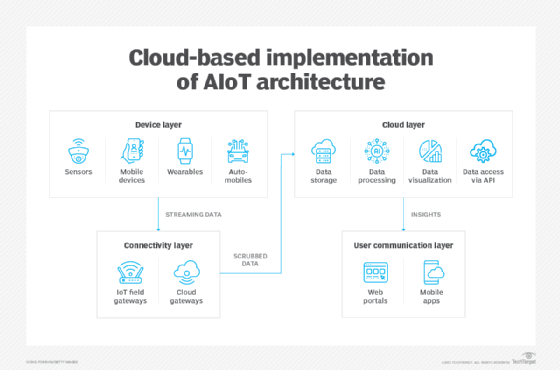
Read MoreWhat is the artificial intelligence of things (AIoT)?
The artificial intelligence of things (AIoT) is the combination of AI technologies and the internet of things (IoT) infrastructure. AIoT’s goal is to create more efficient IoT operations, improve human-machine interactions, and enhance data management and analytics. AI is the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems, and typically uses specialized AI […]
Read MoreWhat is a smart sensor and how does it work?
A smart sensor is a device that takes input from the physical environment and uses built-in compute resources to perform predefined functions when it detects specific input. It can also process data before passing it on. Smart sensors enable more accurate and automated collection of environmental data with less erroneous noise among the accurately recorded […]
Read MoreWhat is internet of things device management (IoT device management)?
Internet of things device management (IoT device management) refers to the processes and tools used to remotely register, configure, provision, maintain and monitor connected devices from a centralized platform. IoT device management tools enable organizations to have better control of their mobile devices, while also ensuring that their devices are kept working, secure and up […]
Read MoreExplore the relationship between IoT governance and privacy
Privacy protection is one of the most critical elements within IoT governance. With IoT devices continuously collecting vast amounts of personal and sensitive data, privacy considerations must be embedded in an organization’s governance structures rather than treated as an afterthought. “Privacy first” should be the message to all who engage in business or personal […]
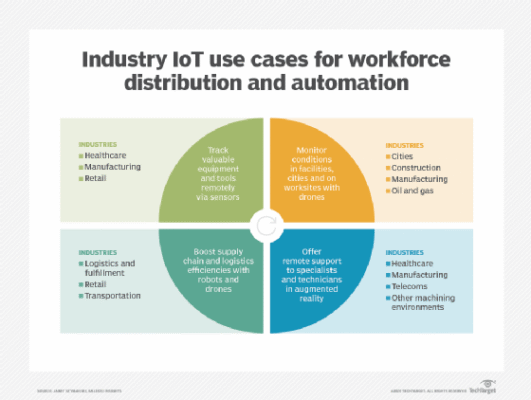
Read MoreTop 12 IoT applications and examples in business
The world now has twice as many connected devices as humans, and the number of IoT-enabled endpoints is expected to climb even more exponentially in the years ahead. In a May 2025 report, German data collection and visualization firm Statista put the number of IoT devices worldwide at 19.8 billion in 2025 and predicted it […]
Read MoreWhat is an IoT gateway?
An IoT gateway is a physical device or software program that serves as the connection point between the cloud and internet of things devices, such as controllers, sensors and smart devices. IoT is used in enterprises and industries and can be found in consumer products. IoT gateways act as a central hub, connecting IoT devices […]
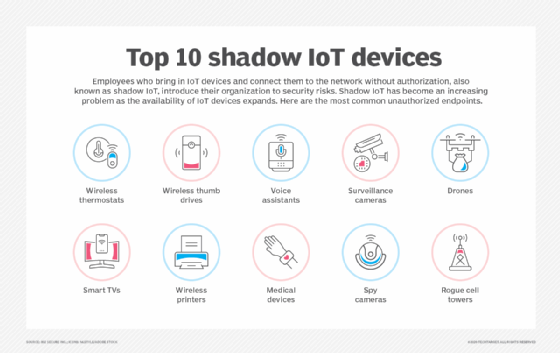
Read More11 IoT security challenges and how to overcome them
From smartwatches to smart streetlights, smart home devices to smart manufacturing, the internet of things has revolutionized how people and organizations operate, improving efficiencies and optimizing processes. With these benefits, however, comes a major challenge: IoT increases the number and types of security risks businesses and consumers face. Any device that connects to the […]
Read More